Understanding Air Hoses and Fittings
Air hoses and fittings are essential components utilized in pneumatic systems, serving as conduits for compressed air to power various air-operated tools and machines. Understanding these components thoroughly enables users to make informed decisions when selecting the right products for their needs, ensuring efficiency and safety during operation. Air hoses and fittings not only impact tool performance but also influence overall productivity in industrial and domestic settings.
What Are Air Hoses and Fittings?
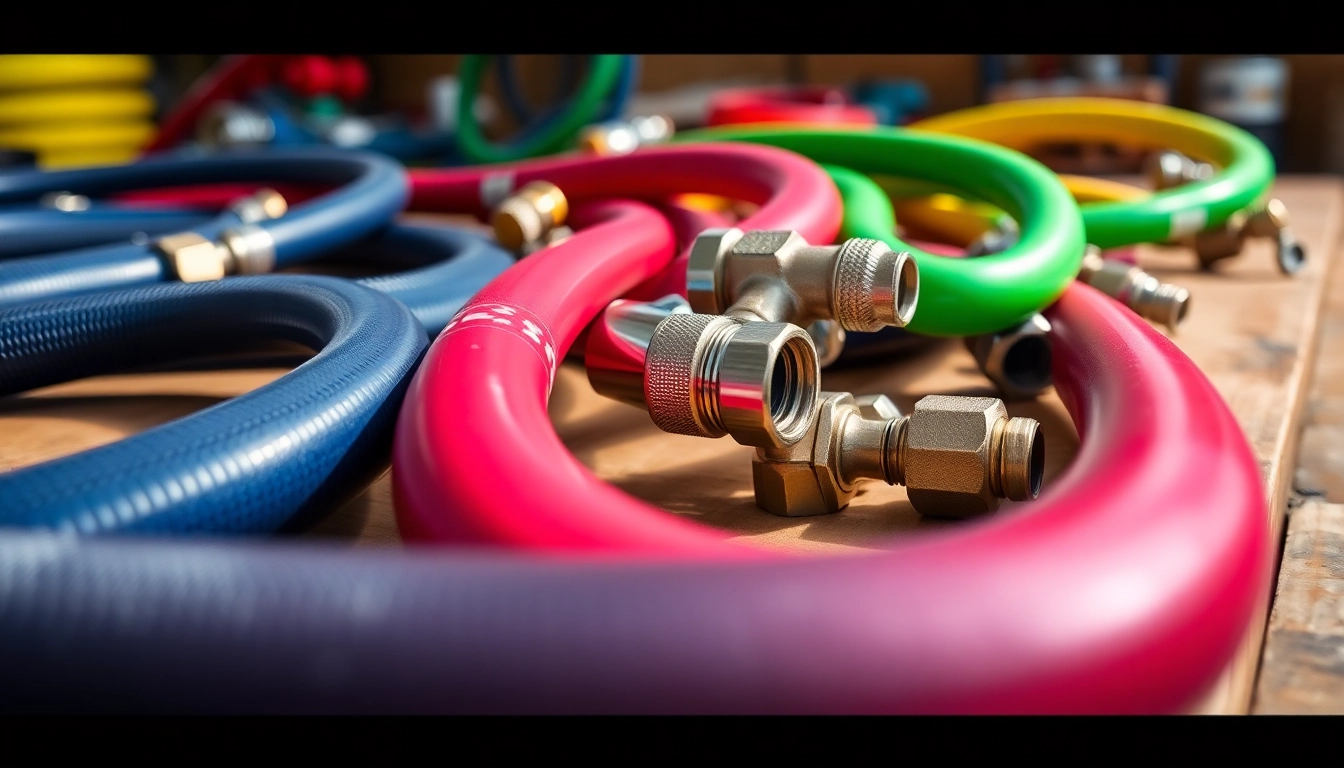
Air hoses are flexible tubes specifically designed to transport compressed air from a compressor to pneumatic tools and devices. The fittings are the connectors that allow these hoses to connect seamlessly to air tools, hoses, and compressors. Together, they create a system that facilitates the efficient use of compressed air across various applications, such as automotive repair, construction, and manufacturing.
The choice of both hoses and fittings must be based on the specific needs of the task at hand, considering factors like length, diameter, material, and intended application to ensure optimal functionality.
Types of Air Hoses
Air hoses come in various configurations and materials, which significantly affect their performance and suitability for different tasks. Here are some common types:
- Rubber Air Hoses: Known for their durability and flexibility, rubber air hoses are ideal for rugged environments. They are resistant to kinking and abrasion, making them suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
- Polyurethane Hoses: Often lighter and more flexible than rubber hoses, polyurethane hoses are ideal for applications requiring maneuverability, such as in workshops. However, they may kink more easily than rubber hoses.
- PVC Hoses: These hoses are abrasion-resistant and can handle various pressures, making them ideal for lighter duty applications. However, they are less flexible, particularly in cold weather.
Benefits of Quality Fittings
The fittings used in air hose systems are crucial for ensuring leaks are minimized, connections are secure, and the system operates efficiently. Quality fittings provide several benefits:
- Leak Prevention: High-quality fittings are designed to create airtight seals to prevent air leaks, which can lead to inefficiencies in performance.
- Durability: Quality fittings made from robust materials can withstand wear and tear, ensuring they remain functional over time and reducing the need for frequent replacements.
- Ease of Use: Features like quick-connect designs enable users to easily attach and detach hoses and tools, increasing productivity.
Choosing the Right Air Hose for Your Needs
Evaluating Material Durability
The material of the air hose plays a significant role in its durability and overall lifespan. For heavy-duty applications, rubber hoses are often favored due to their strength and resistance to environmental factors. In contrast, for light-duty tasks, polyurethane hoses provide a balance between flexibility and sufficient durability. When evaluating hoses, consider the corrosive properties of the environment and whether the hose will be exposed to extreme temperatures.
Size Considerations for Hoses and Fittings
Choosing the correct size for both hoses and fittings is critical to ensuring a seamless flow of compressed air and avoiding pressure losses. Hoses are typically measured by their inside diameter (ID), which should correspond to the specifications of the tools and compressor being used. Fittings also come in various sizes—common dimensions include 1/4-inch and 3/8-inch NPT (National Pipe Thread). Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications when making size decisions.
Common Applications for Air Hoses
Air hoses are used across multiple applications, each requiring specific considerations regarding hose type, size, and fittings. Some common applications include:
- Automotive Repair: Air hoses are vital in operating tools like pneumatic wrenches, nailers, and spray guns.
- HVAC Maintenance: Air hoses support refrigeration and air conditioning systems, where they transport refrigerants and compressed air.
- General Construction: Many construction tasks rely on compressed air for tools, making robust and flexible hoses essential.
Common Types of Air Hose Fittings
Quick Connect Fittings
Quick connect fittings provide an easy and efficient way to join hoses to tools and compressors without the need for threading. They are designed for rapid connection and disconnection, allowing for seamless transitions between tools, which enhances productivity on the job site. Quick connects come in various styles, including industrial interchange, automotive, and agricultural types, catering to a wide range of applications.
Threaded vs. Non-Threaded Fittings
Threaded fittings require the use of threads for connection, ensuring a tight and secure fit. These fittings are often found in permanent installations where the connection is not frequently altered. Non-threaded fittings, commonly seen in quick connect formats, allow for more flexibility and faster changes but may not provide the same level of structural integrity. When choosing between threaded and non-threaded fittings, consider frequency of use and maintenance requirements.
Choosing Couplers and Plugs
Couplers and plugs are vital for creating a secure connection between hoses and tools or equipment. Couplers are typically attached to the end of the air hose and may feature multiple connection options for different tools, while plugs are inserted into the couplers. It’s essential to choose compatible couplers and plugs to ensure the system operates smoothly. Opting for high-quality couplers can enhance airflow efficiency and reduce the risk of leaks.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
How to Properly Install Air Hoses
Proper installation of air hoses is crucial for maximizing performance and safety. Follow these steps for optimal installation:
- Ensure that the air compressor is turned off and disconnected from the power source.
- Choose the appropriate fitting and attach it securely to the hose, ensuring a tight seal.
- Connect the hose to the air tool or compressor, checking for any leaks in the connection.
- Test the system by gradually reintroducing air pressure to the compressor and observing hose behavior.
Signs of Wear in Fittings
Regular inspection of air hose fittings can prevent system failures. Look for signs of wear such as:
- Cracks or deformities along the fitting.
- Excessive leakage of air around connections.
- Corrosion or rust, particularly in metal fittings.
Replacing worn fittings promptly can save costs associated with inefficiency and potential safety hazards.
Maintenance Best Practices
Maintaining air hoses and fittings involves regular cleaning and inspection. Periodically check connections and clean them to remove dust and debris that may affect performance. Always store hoses in a cool, dry place to avoid damage from environmental factors. Proper organization using hose reels can prevent kinking and extend the lifespan of your hoses.
Enhancing Performance with Accessories
Hose Reels and Storage Solutions
Utilizing hose reels not only conserves space but also protects the hose from damage when not in use. Reels allow for easy coiling and uncoiling of hoses, promoting better organization and reducing wear. For home and industrial settings, investing in a high-quality hose reel can drastically improve the longevity of the hose and ease of use.
Adapters and Additional Fittings
Adapters are essential when connecting hoses to devices with different sizes or types of fittings. Having a variety of adapters ensures compatibility across various tools and equipment, which can enhance operational flexibility. Keeping a kit of versatile fittings handy can significantly improve workflow efficiency on worksites.
Improving Airflow Efficiency
To maximize the performance of air hoses, ensuring efficient airflow is critical. This can be obtained by:
- Using the shortest length of hose possible to minimize pressure drop.
- Choosing hoses with adequate diameter for the necessary air flow rate.
- Maintaining fittings in good condition to prevent leaks, as even small leaks can significantly reduce airflow efficiency.