What Are Antioxidants?
Defining Antioxidants and Their Role
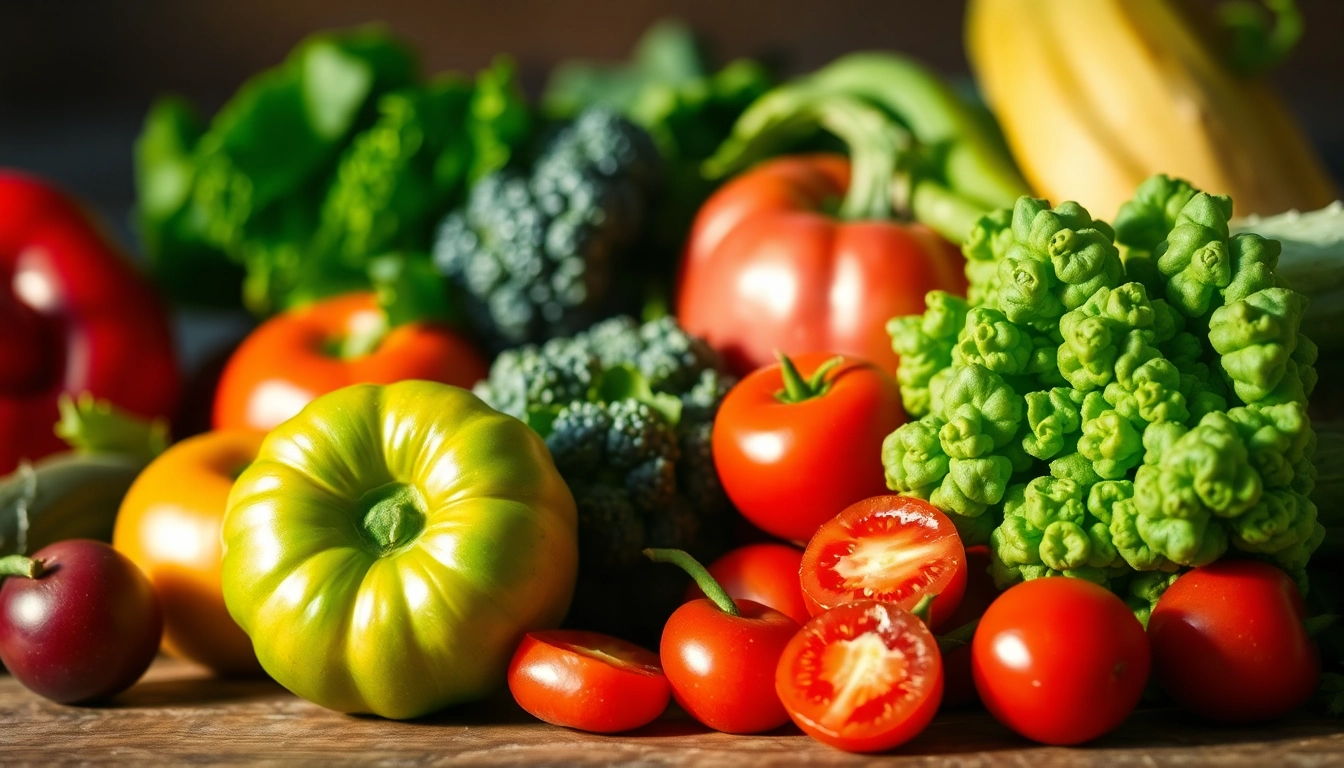
Antioxidants are natural molecules that play a crucial role in protecting our bodies from oxidative stress. These compounds are primarily found in various foods, especially fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. They function by scavenging free radicals—unstable molecules generated during metabolic processes and external factors like pollution and UV radiation. By neutralizing free radicals, antioxidants help prevent cellular damage that could lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and heart disease. Essentially, antioxidants act as protective agents for our body, contributing to overall health and longevity. For a deeper understanding of how antioxidants work, you can refer to various health resources like antioxidants and their impact on health.
Natural vs. Synthetic Antioxidants
Antioxidants can be classified into two main categories: natural and synthetic. Natural antioxidants are found in food sources, with certain vitamins and minerals being prominent examples, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium. On the other hand, synthetic antioxidants are often added to processed foods or available as dietary supplements. While these synthetic forms can still perform antioxidant functions, they may not replicate the effectiveness of their natural counterparts. Studies indicate that naturally occurring antioxidants in foods provide additional beneficial compounds that work synergistically for better health outcomes.
How Antioxidants Combat Free Radicals
Free radicals are molecules with unpaired electrons, making them highly reactive and capable of causing cellular damage. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals and lead to chain reactions that contribute to various chronic diseases. Antioxidants mitigate this damage by donating an electron to free radicals, thus stabilizing them and preventing the damage they cause. This reaction is essential in lowering the risk of oxidative stress and maintaining cellular integrity. Many antioxidants, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, enhance this protective effect by not only neutralizing free radicals but also promoting the body’s own antioxidant defenses.
Health Benefits of Antioxidants
Antioxidants and Disease Prevention
The health benefits of antioxidants extend beyond cellular protection. Numerous studies have linked diets rich in antioxidants with a reduced risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. For instance, the Mediterranean diet, which is abundant in antioxidant-rich foods like olive oil, fruits, and vegetables, has been associated with lower cardiovascular risks. Similarly, antioxidants like vitamins C and E have been shown to mitigate inflammation, which is a risk factor for many chronic diseases. By incorporating a variety of antioxidant-rich foods into your diet, you can significantly enhance your overall health and well-being.
Impact on Aging
Aging is often accompanied by an increase in oxidative stress, which can lead to cellular and tissue damage. Antioxidants are thought to play a vital role in slowing down these aging processes. The notion of “free radical theory of aging” posits that the accumulation of oxidative damage contributes to age-related diseases, declining health, and eventual death. Antioxidants such as glutathione, found in many fruits and vegetables, can help combat this effect, supporting healthy skin, cognitive function, and physical performance as we age. Regular consumption of antioxidants can lead to improved lifespan and quality of life in older adults.
Role in Enhancing Athletic Performance
Athletes are often exposed to higher levels of oxidative stress due to intensified physical exertion, making antioxidants crucial for performance and recovery. Studies have shown that antioxidant supplementation can reduce muscle soreness, enhance recovery, and lower exercise-induced oxidative stress. For example, consuming foods high in vitamin E and C can help athletes recover faster by reducing inflammation and muscle damage. Moreover, antioxidants play a role in energy production by improving blood flow and oxygen delivery to muscles, leading to enhanced endurance and performance.
Food Sources of Antioxidants
Top Fruits and Vegetables High in Antioxidants
Incorporating a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet is one of the best ways to ensure adequate antioxidant intake. Some of the top antioxidant-rich foods include:
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and blackberries are packed with anthocyanins, which are potent antioxidants.
- Dark Chocolate: Rich in flavonoids, dark chocolate provides impressive antioxidant benefits.
- Green Tea: Contains catechins, which can help protect against oxidative damage.
- Leafy Greens: Spinach and kale are high in vitamins A, C, and K, all of which contribute to antioxidant activities.
- Nuts: Walnuts and pecans are excellent sources of antioxidants.
Incorporating Antioxidant-Rich Foods into Your Diet
Integrating antioxidant-rich foods into your daily diet can be both simple and enjoyable. Here are some practical tips:
- Add berries to your morning oatmeal or yogurt.
- Snack on nuts instead of chips or cookies.
- Drink antioxidant-rich green tea as a substitute for sugary beverages.
- Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your meals—each color often indicates a different range of beneficial antioxidants.
- Explore cooking methods that preserve antioxidant levels, such as steaming and stir-frying instead of boiling.
Cooking Methods to Preserve Antioxidant Levels
The cooking process can influence the antioxidant levels in foods. Here are some techniques that help maintain these valuable compounds:
- Steaming: Retains more nutrients compared to boiling, which often causes nutrient loss.
- Sautéing: Using healthy oils can preserve and enhance the antioxidant properties of vegetables.
- Raw Consumption: Many fruits and vegetables, like carrots and bell peppers, can be eaten raw to maximize antioxidant intake.
Understanding Antioxidant Supplements
Are Supplements Effective?
The effectiveness of antioxidant supplements is a topic of debate. While they can provide concentrated doses of antioxidants, research suggests that whole food sources may be more beneficial. This is largely due to the synergistic effects of various nutrients found in food that work together to enhance antioxidant defenses. Some studies have indicated that antioxidant supplements do not provide the same health benefits as those obtained from natural food sources.
Risks and Considerations of Supplementation
Although antioxidant supplements can be beneficial for certain individuals, they are not without risks. High doses of supplements can interfere with the body’s natural defenses or lead to adverse effects. For example, excessive vitamin E supplementation has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding. It’s crucial for individuals to consult healthcare providers before starting any supplementation regimen to evaluate personal health needs and avoid potential interactions.
Choosing the Right Antioxidant Supplement
If one decides to pursue antioxidant supplements, careful consideration should be given to product selection. Here are some guidelines:
- Look for third-party testing to ensure the supplement’s quality and potency.
- Prefer whole-food-based supplements over isolated antioxidants, as they may offer additional benefits.
- Research the forms of antioxidants included in the supplement and their effectiveness.
Future Research on Antioxidants
Current Studies and Findings
Research into antioxidants is ongoing, with scientists exploring their potential in treating various conditions. Recent studies are focusing on understanding the mechanisms behind antioxidant actions in the body, particularly how they may influence chronic diseases and aging. For example, the potential role of antioxidants in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s is a promising area of exploration, as oxidative stress is believed to contribute significantly to the progression of such disorders.
The Potential of New Antioxidant Variants
As research progresses, new antioxidant compounds are being discovered and evaluated for their health benefits. For instance, recent studies on the antioxidant potential of compounds found in spices like turmeric and ginger have gained interest, highlighting their anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, ongoing investigations on synthetic antioxidants aim to develop more effective formulations that can be beneficial in clinical settings.
What the Future Holds for Antioxidant Research
The future of antioxidant research holds promise as scientists continue to uncover new applications and benefits. The integration of advanced technology in molecular biology is allowing for more precise studies on how antioxidants interact within the human body. As more is learned, the potential for antioxidants in preventive medicine and health maintenance looks increasingly encouraging. The challenge will be to translate these findings into effective dietary guidelines and health practices that can benefit the broader population.